Table of Contents
How Quickly do Gallstones Grow in Older Adults?
The gallbladder is an organ that stores the bile juice that is produced by the liver.
Gallstones are formed when deposits of bile or cholesterol harden in the gall bladder, and they may be caused by abnormally high concentrations of bile juice or cholesterol.
Summary
- Pains due to the presence of gallstones in the gallbladder occurs in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen
- Most patients suffering from gallstones are asymptomatic
- The prevalence increases with age
- Women are at an increased risk of developing gallstones
How do gallstones cause problems?
In some individuals, gallstones do not cause problems and do not require management because they are asymptomatic and may only be detected during abdominal scans, but a few numbers of individuals have experienced serious complications.
Gallstones may cause problems in the following way:
Case 1:
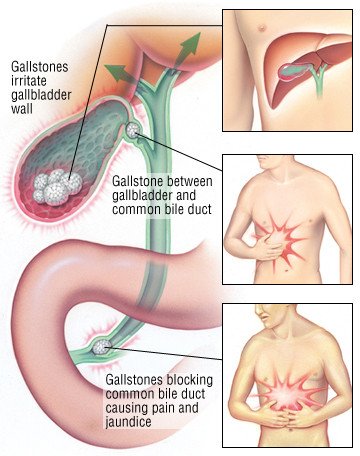
Gallstones in the gallbladder (Cholelithiasis): The gallbladder may contract, forcing the gallstones against the gallbladder outlet. This results in intermittent abdominal pain which usually resolves within a few hours when the stone falls back into the gallbladder.
The following life-threatening scenarios may cause persistent pain to the individual:
- The stone may get stuck in the gallbladder outlet
- It may result in gallbladder inflammation
- If untreated, it may progress to severe infection and even cause the gallbladder to burst.
Case 2:
Gallstones in the common bile duct (Choledocholithiasis): Gallstones might leave the gallbladder outlet and get trapped in the common bile duct leading to bile duct obstruction. This may in turn cause pains, fever, yellow coloration of the skin, and vomiting.
Case 3
Gallstones in the pancreatic duct (Cholecystitis): Gallstones in the bile duct may obstruct the pancreatic duct, causing inflammation of the pancreas, this is known as pancreatitis and may cause pain in the abdomen, this pain may shift to the back and cause vomiting.
Case 4
Acute cholangitis: Acute cholangitis occurs when there is a bacteria infection on the biliary tree, and this can lead to pains and causes jaundice.
https://www.drugs.com/health-guide/images/f78db7cd-7927-42d4-b853-8ecb74b00da3.jpg
Risk factors associated with developing gallstones
A person is at risk of developing gallstones due to:
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Pregnancy
- Birth control pills or hormonal pills
Types of gallstones
- Cholesterol gallstones are light-coloured stones, mainly caused by cholesterol.
- Pigment gallstones are usually dark-coloured and caused by bilirubin.
Signs and symptoms of gallstones
Signs and symptoms of gallstones occur as stones traverse through the biliary tree.
- Signs and symptoms of Cholelithiasis:
- Pain in the right upper quadrant and epigastrium. The pain occurs after eating fatty or greasy foods and it lasts for about 1 – 5 hours.
- Bloating
- Belching
- Indigestion
- Signs and symptoms of cholecystitis
- Pains are more localized and last for more than 6 hours
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fever and chills
- Diaphoresis
- Tachycardia
- Signs and symptoms of choledocholithiasis
- Jaundice due to hyperbilirubinemia
- Urine and stool changes colour
- Pruritus – itching sensation due to retention of bile salts
- Enlarged gallbladder
- Liver inflammation
- Hypotension
- Fever and chills
- Signs and symptoms of acute cholangitis
- Jaundice
- Severe right upper quadrant tenderness
- Fever and chills
- Hypotension
- Altered mental status
When to see a doctor
When you have abdominal pain which does not stop or is recurrent.
It is difficult to diagnose gallstone problems based on symptoms alone as other conditions may cause similar symptoms. If the doctor suspects a case of gallstones, you may be referred to a gastroenterologist who is a doctor that specializes in managing gallstones and other digestive problems.
Your gastroenterologist may order further tests which will determine the severity of your problem and discuss the best treatment options available with you.
Treatment of gallstones
As many as 80% of patients with gallstones do not experience symptoms and hence do not require any treatment. If gallstones cause problems, treatment may be required depending on the case.
Treatment options include:
- Antibiotics: when the gallstones cause gallbladder inflammation, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
- Endoscopic gallstone removal: if the gallstones cause blockages of the bile duct or the pancreatic duct, an endoscopic procedure may be required to remove the gallstones, and this can be done in two ways, namely.
- Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy: in this procedure of removing gallstones, shockwaves are targeted towards the stones to break them.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: This is the removal of stones from the bile duct using an endoscope. In this method, a stent is placed to facilitate the flow of bile and stones into the intestine.
- Surgical gallbladder removal: Some cases require surgery for treatment. The surgery will remove the gallbladder and also treat or repair any other complications. Ultimately, surgery is the definitive treatment to prevent gallstones from forming again and this is commonly done by keyhole surgery. This removal has a little impact on your digestive functions, but some patients can eat normally after gallbladder removal.
Surgical treatment can be carried out in two ways, namely:
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy: This is keyhole surgery, and it is used to remove the gallbladder. In laparoscopic cholecystectomy surgery, patients experience quick recovery from the surgery.
- Open cholecystectomy: In open cholecystectomy, an incision is made to remove the gallbladder, and the patient experiences slow recovery from the surgery.
Ways to prevent gallstones
- Exercise regularly
- Eat healthy
- Maintain healthy body weight
Read also: Negative Effects of Dehydration in Older Adults
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How quickly can gallstones grow?
Gallstones grow at a varying rate, it may take years to grow in the gallbladder.
What can worsen gallstones?
Gallstones can be worsened by eating fatty or greasy foods
Final thought
If you or your loved ones are experiencing persistent symptoms of abdominal pain, speak to your doctor. Do not attempt to self-diagnose and treat.
Featured images from freepik.com by rawpixel.com.