Table of Contents
All About Vascular Dementia in Older Adults
Vascular refers to blood carrying vessels and dementia refers to difficulty with memory, communicating and learning new things.
Vascular dementia is the second commonest type of dementia after Alzheimer’s disease.
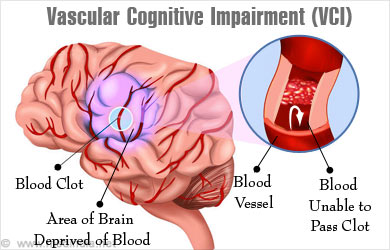
Vascular dementia is a progressive loss of brain function caused by poor blood flow to the brain, typically because of a series of strokes.
Summary
- Vascular dementia accounts for about 15 – 20% of all dementia cases and it occurs when the blood vessels that carries blood to the brain have been destroyed.
- Vascular dementia is more common in men than women and is also more common in African Americans and Asians.
- The risk of having vascular dementia is increased two times after suffering from stroke, and the prevention of stroke or recurrent stroke remains a cornerstone in the prevention of vascular dementia.
- There are many types of vascular dementia, but we basically have two types of vascular dementia namely: multi-infarct dementia and Binswanger’s disease.
https://www.medindia.net/patients/patientinfo/images/vascular-dementia.jpg
What increases the risk of Vascular Dementia?
- High blood pressure: High blood pressure affects blood vessels. Uncontrolled blood pressure causes plaques to build up in the arteries and reduces the efficiency of the arteries to carry blood to the brain and this can affect the way an older adult speaks, sees, thinks, or remembers things.
- Smoking of tobacco products: smoking of tobacco products for example cigarettes tightens and affects blood vessels that carries blood to the brain, depriving the brain of oxygen and essential nutrients that helps the brain to function properly. Smoking of cigarettes causes the blood to clot in the brain and clotting of the blood in the brain results to stroke; which is one of the major causes of vascular dementia.
- Diabetes: Too much sugar in the blood decreases the elasticity of the artery, thereby reducing blood flow to the brain. Restricted blood flow could lead to strokes and vascular dementia.
- High cholesterol: The accumulation of fats and high level of cholesterol can lead to a disease known as atherosclerosis. The accumulation of cholesterol plaque in the walls of arteries causes obstruction of blood flow. When the plaques rupture, it causes acute occlusion of the artery by clot, thereby, restricting adequate flow of oxygen and essential nutrients to the brain.
- Genetic disorder: when there is a mutation in the Notch3 gene it results to vascular dementia. Notch3 gene encodes a single-pass transmembrane receptor and when this genetic mutation occurs, it causes CADASIL which destroys the blood vessels that carries blood to the brain.
Causes of vascular dementia in older adults
Vascular dementia develops in some individuals when atherosclerosis starts to form in the arteries. That is when there is a build up of plaques that thickens and hardens the artery wall. When this process affects the arteries supplying the brain, like the carotid arteries, it leads to a gradual decrease in blood flow to the brain- which is called chronic ischaemia.
Sometimes some parts of the plaques can break away and these bits can drift up towards the brain and can then eventually block a smaller artery, completely stopping the blood supply to the part of the brain that is supplied by that artery.
Other times, the tiny perforating arteries can get completely blocked off by plaque growing within them as a result of atherosclerosis. Regardless of the cause, once blood supply to the brain falls below the demands of the tissue, it is considered as an ischemic stroke.
The tissue damage from an ischemic stroke is usually permanent because the tissue gets damaged, and the dead tissue liquefies in a process called liquefactive necrosis.
Brain tissue necrosis leads to a loss of mental functions governed by that area. If another stroke happens later, more brain tissue might die off and over time this damage worsens. The result is dementia, a persistent loss of mental functions that is severe enough to affect a person’s daily functioning.
Symptoms of vascular dementia in older adults
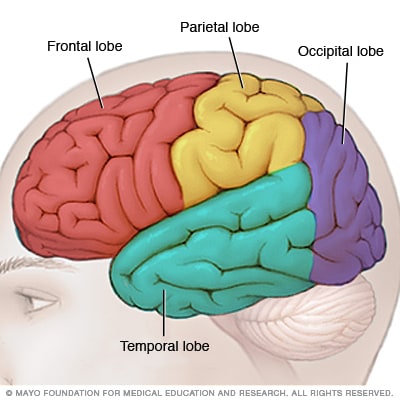
Symptoms of vascular dementia varies depending on which region of the brain is damaged. For example:
- Individuals that have stroke in the temporal lobe of the brain, exhibit symptoms such as: Difficulty to remember things, Hearing problems and difficulty to recognize faces.
- Individuals that have stroke in the frontal lobe of the brain, will exhibit symptoms such as: Having trouble in movement, change in personality, difficulty to spell and count and difficulty in decision making.
- Individuals that have stroke in the parietal lobe of the brain, will exhibit symptoms such as: loss of speech (Aphasia) and Sensory problems.
- Individuals that have stroke in the occipital lobe of the brain, will exhibit symptoms such as: Difficulty in processing visual information.
Types of vascular dementia in older adults
There are many types of vascular dementia, but we basically have two main types namely:
- Multi – infarct vascular dementia
- Binswanger’s disease or subcortical vascular dementia
Multi-infarct vascular dementia: multi-infarct vascular dementia is a type of vascular dementia caused by series of stroke or recurrent strokes (disruption of blood flow to the brain). It is the most common type of vascular dementia. The blood vessels that carry blood to the brain become blocked, disruption of blood flow occurs and this in turn causes damage to the brain. The stroke may not be noticeable, and the individual may not have any symptom of stroke.
In some cases where there are symptoms, these symptoms may last for a few hours, these types are called mini stroke or transient ischaemic attack. Mini stroke or Transient ischaemic attack may happen when the plaques that blocks the blood vessels clears itself within some hours.
If the blood flow to the brain have been disrupted for longer period, it may lead to the death of the affected part of the brain known as infarct. When the damage occurs in multiple tissues in the brain, it is called multi-infarct vascular dementia.
Binswanger’s disease or subcortical vascular dementia: This type of dementia is caused by plaques that affects the small blood vessels in the brain, there is thickening of the arteries, and this may lead to reduced blood flow to the brain. Binswanger’s disease or subcortical vascular dementia are characterized by the diseases that often damages the nerve fibres that carries signals to the brain known as the “white lesions”. This disease causes more damage to the brain than the damages caused by multi-infarct vascular dementia.
Diagnosis of vascular dementia in older adults
Neuropsychological tests, like the mini mental state exam, can be used to confirm that there is a loss of brain function. The vascular cause can be diagnosed using brain imaging, most commonly CT or MRI, which will show multiple cortical and subcortical infarcts and changes like atrophy of the brain cortex, confirming the ischaemia.
Management of vascular dementia in older adults
There is no cure or approved medications for treating vascular dementia, but vascular dementia can be prevented by:
- Controlling the risk factors of stroke and this risk factors includes blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes, and clots.
- Use of cholinesterase inhibitors for example Donepezil or Aricept and Memantine or Namenda
- Treatment of psychiatric symptoms for example depression
- Supporting the patient
Read also: How to prevent cognitive decline in Older Adults
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between dementia and Vascular dementia?
Dementia and Vascular dementia differ in the cause of the resulting dementia, vascular dementia has to do with blood flow restriction that may lead to stroke and dementia. Dementia may be caused by a lot of other factors.
What lifestyle factors can help reduce vascular dementia?
Lifestyle factors that can help reduce vascular dementia are: Daily exercise, eating healthy, staying active both mentally and socially.
What type of doctor should be consulted when an older adult has vascular dementia?
An experienced psychiatrist should be consulted, and a neurologist can be consulted.
Final thoughts
Since vascular dementia is caused mainly by stroke, older adults should endeavour to live a healthy life that is free from risk of developing stoke.
Featured images from pexel.com by Kindel Media.

